
Aug 15, 2016 | Blog
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
AUGUST 15, 2016

Ocelot, photo US FWS
TUCSON, Ariz. – The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service released a recovery plan that will guide restoration and protection of the ocelot populations in Arizona and Texas and in bordering Mexican states of Sonora and Tamaulipas. The ultimate goal of the plan is to increase the number of ocelots in both nations, protect their habitat and create connecting habitat corridors between Arizona and Sonora and between Texas and Tamaulipas. This unique endangered cat ranges as far south as Argentina, but in the U.S. is found only in two small areas of Arizona and Texas.
Statement by Rob Peters, senior Southwest representative for Defenders of Wildlife
“It is encouraging to see a plan that sets quantitative targets for ocelot recovery – 1,200 animals in the Texas-Tamaulipas area and 1,000 in the Arizona-Sonora. To reach these targets, wildlife agencies must decrease deaths and increase important thorn scrub habitat, goals that will require funding and binational cooperation. A serious question is whether there is the political will to provide the necessary resources and limit development.
“Big threats to ocelot recovery in the U.S. include giant open-pit mines like the Rosemont and Hermosa proposed in ocelot habitat in Arizona. In south Texas, three huge liquefied natural gas export terminals are planned right next to the Atascosa National Wildlife Refuge. One terminal would sit on – and possibly sever – an ocelot travel corridor identified by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as vital to the recovery of the ocelot population in Texas. This recovery plan is a starting point, but it will only succeed if harmful developments are stopped and sufficient resources are provided for key conservation actions. Defenders will vigilantly monitor proposed development activities that threaten the future of the ocelot in the United States.”
Background:
U.S. ocelot populations, once extending into Arkansas and Louisiana, have shrunk to a small patch of southern Texas, with perhaps 50 animals, and southern Arizona, where only five animals have been detected since 2009. Ocelots, found in every country south of the United States except Chile, are endangered throughout their range. Some 95 percent of the cats’ native habitat in the U.S. has become urbanized or has been converted to agriculture.
Listed under the Endangered Species Act in 1982 as endangered, the species was initially pushed to the brink of extinction due to habitat loss and overhunting. Now, collisions with vehicles and insufficient habitat are keeping ocelot population numbers in the U.S. low. Mines and liquefied natural gas plants are important new threats.

May 8, 2015 | Blog

Toxic overflow from the historic Lead Queen mine in the Patagonia Mountains drains towards Harshaw Creek.
The Coronado National Forest, Sierra Vista Ranger District hosted a community meeting in Patagonia, Arizona on April 28. The Lead Queen Mine cleanup plan was by presented by Floyd Gray of United States Geological Survey (USGS), and Eli Curiel of the Forest Service.
The Lead Queen was an underground mine for lead, silver, zinc, copper and gold that started in 1898 and was abandoned after 1940. After heavy rains in September 2014, members of PARA discovered and reported the leaking mine site, located approximately 6 miles south of Patagonia, Arizona. In December, the Arizona Department of Environmental Quality served the Forest Service with two notices of violation for the toxic mine spill. The Forest Service issued a “Time Critical Removal Action Approval Memorandum” in February to mitigate the spill and its potential threats to public health and welfare, water and wildlife. Clean up was scheduled to start Spring 2015, before monsoon rains could potentially wash contamination further downstream.
Floyd Gray gave an overview of his findings from sampling and testing the water, soil, and waste rock around the abandoned mine site. It was also deduced that there is more than one source of leakage from the mine site. One source was identified by its extreme concentration of iron while the other source is high in aluminum. All of the tested samples came back with very high levels of contamination from hazardous heavy metals such as arsenic and lead. In one water sample, the heavy metal levels were 20 times higher than the allowable drinking water standards. It was also determined that the mine contamination traveled 9/10th of a mile downstream.
The studies at the Lead Queen site to determine all of the sources of contamination has lead to a larger, ongoing study of the watersheds in the Patagonia Mountains by USGS and the Forest Service.
Eli Curiel detailed the plans to plug the six abandoned tunnels and shafts of the Lead Queen mine site with polyurethane foam. The waste rock piles laced with toxic heavy metals will be consolidated into a new location above the watershed and capped with clean fill to prevent future contamination. The polluted sediment in the waterway will be removed with the aid of a series of eleven gabion walls across the drainage filled with zeolite to capture and hold the heavy metals. The clean up area comprises five acres on the Coronado National Forest in the Patagonia Mountains. The mine site will require ongoing monitoring and maintenance, essentially forever.
The cost to taxpayers has not yet been determined. The clean up project has not yet gone out to bid. It’s expected to take up to 120 days with work possibly starting this summer.
More information can be obtained from the Forest Service Project On-Scene Coordinator, Eli Curiel at 520-388-8413.
Regal Resources Sunnyside Mine Exploration

Mexican Spotted Owl ©Gooch Goodwin
At the public meeting, an update was given on Regal Resources’ Sunnyside mining exploration project in the Patagonia Mountains by Forest Service Geologist Mindy Vogel. Conspicuously absent from Vogel’s overview was the ongoing litigation between Defenders of Wildlife and PARA against the Forest Service and US Fish and Wildlife for the unlawful approval of this project.
For the present time, no work is allowed at the Sunnyside site between March 1 and Oct 1, 2015 because of nesting Mexican spotted owls and Yellow-billed cuckoos in the area, according to the Forest Service Decision Memo.
No questions were permitted during any of the presentations. Audience members were required to seek out Forest Service and USGS personnel after all presentations were complete to ask questions. It is a format that we find effectively prevents members of the community from getting all of their questions answered and learning the most information possible.
Wildcat Silver Hermosa Proposal
Forest Service geologist Margie DeRose gave an overview and an update of the expected timeline of the AZ Mining Inc (aka Wildcat Silver, AMI) Hermosa mining exploration proposal in the Patagonia Mountains on the Coronado National Forest. The final Environmental Assessment and draft decision is estimated for release in October 2015 – over a year past the original timeline. A 45 day public objection period will follow.
Meanwhile, AZ Mining Inc / Wildcat Silver board chairman Richard Warke is privately funding more mine exploration drilling on their privately owned land. AZ Mining Inc / Wildcat Silver is now claiming that deposits for lead, zinc and silver exist for an additional mine at the Hermosa project, referred to as Hermosa North West.

Apr 27, 2015 | Blog
New Decision Memorandum Issued for Sunnyside Mineral Drilling Project in Patagonia Mountains
 The Forest Service sent out a notice on April 10th that a new Decision Memo has been issued for the Regal Resources Sunnyside project, an exploratory mineral drilling proposal in the Humboldt Canyon and Alum Gulch areas of the Patagonia Mountains on the Coronado National Forest.
The Forest Service sent out a notice on April 10th that a new Decision Memo has been issued for the Regal Resources Sunnyside project, an exploratory mineral drilling proposal in the Humboldt Canyon and Alum Gulch areas of the Patagonia Mountains on the Coronado National Forest.
The emailed notice from the Forest Service stated that exploratory drilling can start once “the operator provides a reclamation performance bond, incorporates the design features from the decision document, and the Plan of Operations is approved.”
The notice is misleading because it fails to mention two important facts.
No drilling can take place between March 1 to September 30 to avoid potential disturbance to the Mexican spotted owl and Yellow-billed cuckoo during their breeding season, as stated in the Decision Memo.
Additionally, PARA and Defenders of Wildlife are still in litigation against the Forest Service and US Fish and Wildlife Service for this unlawful approval of the Sunnyside Proposal. Read more…
The Sunnyside mineral drilling proposal is located approximately 7 miles south of the town of Patagonia. For more information concerning this decision, please contact Mindy Sue Vogel, Geologist, Coronado National Forest, 300 W. Congress Street, Tucson, AZ 85701, 520-388-8327, msvogel@fs.fed.us.

Oct 29, 2014 | Blog
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
October 29, 2014
Contact: Courtney Sexton, csexton@defenders.org, 202-772-0253
Wendy Russell, wendy@patagoniaalliance.org, 520-477-2308
Groups file complaint against Forest Service and Fish and Wildlife Service for approval of mineral drilling project in Arizona’s Coronado National Forest
TUCSON, ARIZ. – Defenders of Wildlife and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance today asked a federal court to hold the United States Forest Service and United States Fish and Wildlife Service accountable for their unlawful approval of the “Sunnyside” mineral exploration drilling project in southern Arizona’s Coronado National Forest, in the Alum Gulch area of the Patagonia Mountains. The groups say the approval of the Canadian mining company Regal Resources’ Sunnyside Project violates environmental laws and poses a potential threat to endangered species and the safety of drinking water for local residents. The Sunnyside Project involves drilling multiple exploratory holes up to 6,500 feet deep in one of the most biologically diverse mountain ranges in Arizona. The extensive drilling and construction would run 24/7 for months on end, and the total project operations could last up to 3 years.

Mexican spotted owl, ©Gooch Goodwin
The Coronado National Forest, the Patagonia Mountains and the watersheds in this region support some of the world’s most imperiled wildlife, including the jaguar, ocelot, lesser long-nosed bat, Mexican spotted owl, and yellow-billed cuckoo. Of particular concern is the Mexican spotted owl “Protected Activity Center” (PAC) in the Alum Gulch area, a site which is supposed to have the greatest protection of the law. One of the project’s proposed drilling sites is only one-tenth of a mile from the “nesting core area” of this PAC.
“The potential damage from the Sunnyside Project, especially coupled with other damaging mining projects in the region, could have devastating impacts on this imperiled wildlife and the habitat they depend on, as well as the water supply for local residents,” said Rob Peters of Defenders of Wildlife. “This is a national forest and imperiled wildlife and their habitats on the forest should be protected— not polluted by expanded drilling operations.”

Ocelot, Leopardus pardalis. photo US FWS
Patagonia area residents are dependent on water originating from Alum Gulch, an area which is also designated as critical habitat for the jaguar and Mexican spotted owl. The imperiled ocelot, lesser long-nosed bat, and yellow-billed cuckoo have also been observed near the project area.
“The Sunnyside Project could have tremendous adverse impacts on local wildlife and local residents, affecting the floodplains and the municipal watershed of the town of Patagonia,” said Wendy Russell of the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance. “The drilling will require 12,500 gallons of water per day, an amount approximately equal to ten percent of the daily water usage of the Town of Patagonia. This project threatens not only endangered wildlife, but our community’s water, health and safety.”
Click to hear from environmental attorneys on why they sue.
###
Defenders of Wildlife is dedicated to the protection of all native animals and plants in their natural communities. With more than 1.1 million members and activists, Defenders of Wildlife is a leading advocate for innovative solutions to safeguard our wildlife heritage for generations to come. For more information, visit www.defenders.org and follow us on Twitter @DefendersNews.
The Patagonia Area Resource Alliance is a citizen watchdog organization that monitors the activities of mining companies, as well as ensures government agencies’ due diligence, to make sure their actions have long-term, sustainable benefits to our public lands, our water, and the town of Patagonia. For more information visit www.patagoniaalliance.org and follow us on Twitter @PARAalliance.

Oct 8, 2014 | Blog
For Immediate Release
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
October 02, 2014
Sacramento – The western population of the yellow-billed cuckoo will be protected as a threatened species under the Endangered Species Act (ESA), the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service announced today. The Service determined that listing a distinct population segment (DPS) of the bird in portions of 12 western states, Canada and Mexico is warranted. In the U.S., the DPS will cover parts of Arizona, California, Colorado, Idaho, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, Wyoming, Montana, Oregon and Washington.
 The western population of the yellow-billed cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus), an insect-eating bird found in riparian woodland habitats, winters in South America and breeds in western North America. Once abundant in the western United States, populations have declined for several decades, primarily due to the severe loss, degradation and fragmentation of its riparian habitat as a result of conversion to agriculture, dam construction, river flow management and riverbank protection. Overgrazing and invasive exotic plants have also contributed to declines.
The western population of the yellow-billed cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus), an insect-eating bird found in riparian woodland habitats, winters in South America and breeds in western North America. Once abundant in the western United States, populations have declined for several decades, primarily due to the severe loss, degradation and fragmentation of its riparian habitat as a result of conversion to agriculture, dam construction, river flow management and riverbank protection. Overgrazing and invasive exotic plants have also contributed to declines.
“While the major threat to yellow-billed cuckoos has been loss of riverside habitat, we do not anticipate any significant new water-related requirements as a result of this listing decision,” said Ren Lohoefener, Director of the Service’s Pacific Southwest Region. “The water resource requirements for riparian habitat are not unique to cuckoos, and in many cases are already being implemented for other species. Riparian restoration efforts go hand-in-hand with good land management, especially management that promotes good livestock grazing practices.”
The Service’s final listing rule, which will be published in tomorrow’s Federal Register and become effective November 3, 2014, is based on a thorough review of the best scientific and commercial information available, obtained through exhaustive research, public comments and independent scientific peer reviews.
Next steps include designation of critical habitat for the species and development of a recovery plan. Both steps will be strengthened by participation from other federal and state agencies, tribal entities and the public in the open comment periods.
More information, including the listing rule, is at: http://www.fws.gov/sacramento/outreach/Public-Advisories/WesternYellow-BilledCuckoo/outreach_PA_Western-Yellow-Billed-Cuckoo.htm
Proposed Critical Cuckoo Habitat Near Patagonia, Arizona.
Critical habitat for the Yellow-billed cuckoo is proposed from the Town of Patagonia west along Sonoita Creek and includes Patagonia Lake and the Sonoita Creek State Natural Area. That area is the only proposed critical habitat near Patagonia, Arizona. The effect of this regulation, if finalized, is to designate critical habitat for the western yellow-billed cuckoo under the Endangered Species Act.
FWS is seeking comments on the designation of critical habitat for Western Yellow-billed cuckoos. Deadline to comment is October 14, 2014.
Follow link to submit comments: https://www.federalregister.gov/articles/2014/08/15/2014-19178/endangered-and-threatened-wildlife-and-plants-designation-of-critical-habitat-for-the-western
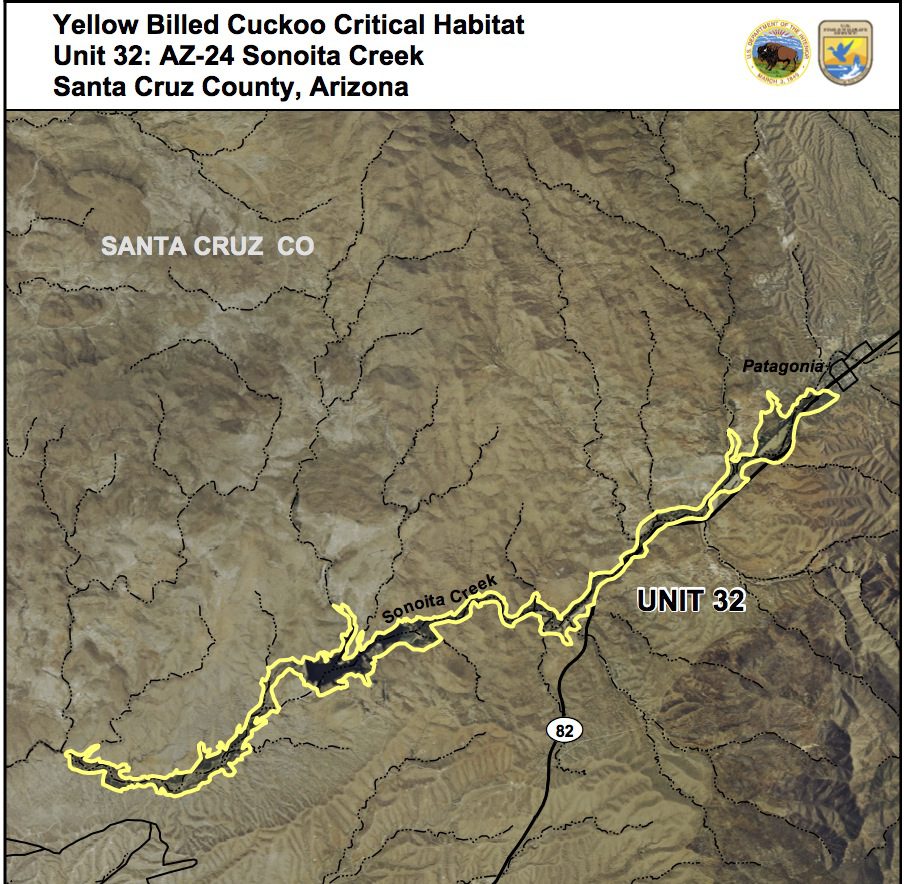
Sonoita Creek Cuckoo Proposed Habitat: Unit 32_AZ_24
The mission of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service is working with others to conserve, protect, and enhance fish, wildlife, plants, and their habitats for the continuing benefit of the American people. We are both a leader and trusted partner in fish and wildlife conservation, known for our scientific excellence, stewardship of lands and natural resources, dedicated professionals, and commitment to public service. For more information on our work and the people who make it happen, visit www.fws.gov/mountain-prairie.









 The western population of the yellow-billed cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus), an insect-eating bird found in riparian woodland habitats, winters in South America and breeds in western North America. Once abundant in the western United States, populations have declined for several decades, primarily due to the severe loss, degradation and fragmentation of its riparian habitat as a result of conversion to agriculture, dam construction, river flow management and riverbank protection. Overgrazing and invasive exotic plants have also contributed to declines.
The western population of the yellow-billed cuckoo (Coccyzus americanus), an insect-eating bird found in riparian woodland habitats, winters in South America and breeds in western North America. Once abundant in the western United States, populations have declined for several decades, primarily due to the severe loss, degradation and fragmentation of its riparian habitat as a result of conversion to agriculture, dam construction, river flow management and riverbank protection. Overgrazing and invasive exotic plants have also contributed to declines.









