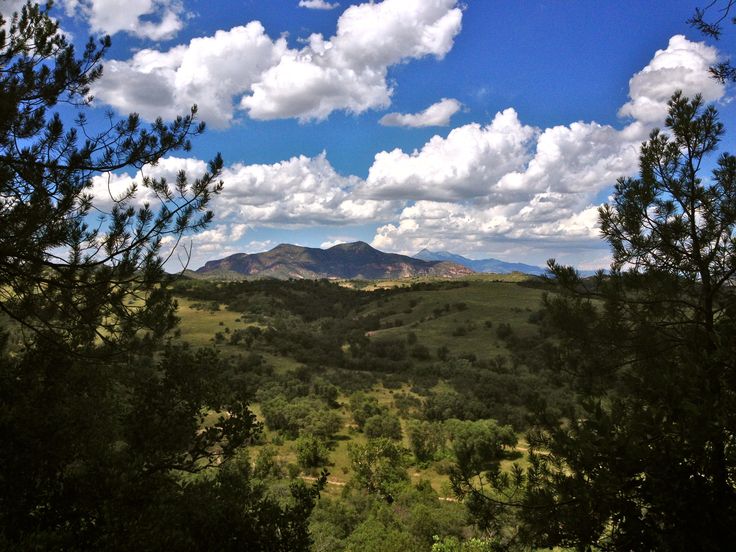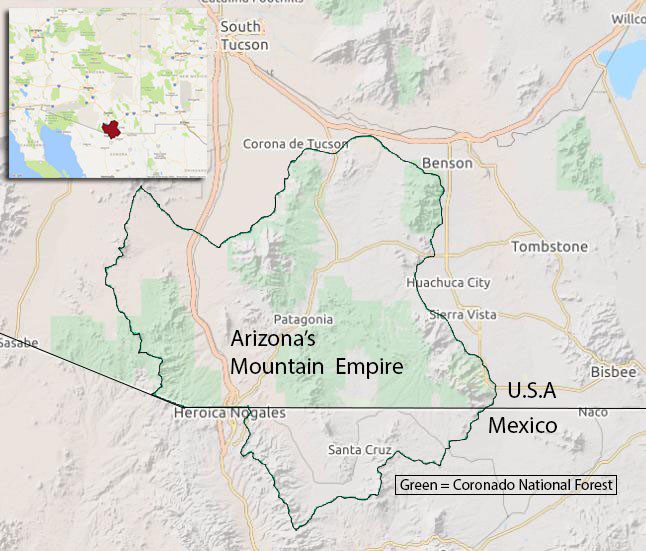
Southern Arizona’s Mountain Empire: Sanctuary for Rare and Unusual Species
Imagine a little-known national treasure — a largely wild land home to ocelots, exotic and imperiled birds like elegant trogons and Mexican spotted owls, imperiled reptiles and amphibians like the threatened Chiricuahua leopard frog, and El Jefe, the only jaguar currently living in the United States. This is the Mountain Empire of southern Arizona, a place as special as Yosemite or Yellowstone, and worthy of international recognition. Extending across the border into northern Sonora, Mexico, this region is bounded by mountains that rise from the flat desert floor to touch the sky. With one of the richest concentrations of biodiversity in the U.S., the Mountain Empire is a sanctuary for imperiled species. But even a sanctuary can be threatened.

Mountain Empire, © Thunderforest
Refuges in the Sky
One reason the Mountain Empire has so many rare and unique species is the rugged sky island mountain ranges. Each range, like the iconic Santa Rita Mountains, south of Tucson, stands alone surrounded by desert flatlands like an island in the sea, with mountains so tall that they span climate zones from hot, dry desert to moist forests at higher altitudes. Together, these characteristics give the mountains their nicknames of “sky islands.” For many species, the sky islands are refuges where human impacts have been relatively small. Streams rise from the rocks, nurturing rare fish, frogs, snakes, and nesting habitat for birds like threatened yellow-billed cuckoos, southwestern willow fly catchers and hummingbirds.

Western yellow-billed cuckoo, © Creed Clayton/USFWS
There are so many hummingbird species in the Mountain Empire that the Tucson Audubon Society founded the Paton Hummingbird Center, dedicated to conserving hummingbirds and other local biodiversity.
Birders visit from countries around the world for the chance to see so many species in one place. One of Defenders’ board members, Dr. Ron Pulliam, works with the Mountain Empire group Borderlands Restoration to restore the plants that hummingbirds, bees, butterflies, and moths need along Harshaw and Sonoita Creeks in the Patagonia Mountains. The globally imperiled Patagonia eyed silk moth, once widespread in native grasslands, is now making its last U.S. stand in the Patagonia Mountains. The threatened southwestern willow flycatcher, once common near Tucson in now-vanished gallery forest along the Santa Cruz River, is today found higher up in riparian vegetation along still-flowing mountain streams.
One of the gems of the Mountain Empire is the Las Cienegas National Conservation Area: 45,000 acres of rolling grasslands, oak-studded hills, along with the Cienegas Creek wetlands. This is home to the world’s largest population of endangered Gila topminnow and other federally threatened and endangered fish, frogs and snakes. Las Cienegas provides a vital corridor of protected lands that connects the Santa Rita and Whetstone sky islands.
The most revered animal in the Mountain Empire is El Jefe, a powerful male jaguar. Video of him prowling along a stream in the Santa Rita Mountains recently went viral, with at least 20 million viewers. He and other jaguars and ocelots most likely came north to the U.S. from Sonora, Mexico in the past decade, travelling along sky island mountain corridors with little human activity.

Jaguar, © Barry Draper
Threats to the Empire
Sadly, as much healthy habitat as there is in this region, there’s also a problem: Industrial mining. The Mountain Empire is riddled with old abandoned mines and grandiose plans for new ones. As you can imagine, mining has a massive impact on an ecosystem, from the land itself, to the noise that can scare wildlife away, to the traffic that would come in and out of the mining project. And perhaps most importantly, there’s the water.
Throughout the Southwest, so much groundwater has been pumped for agriculture, industry, and towns and cities that water tables have dropped and streams and ponds have dried up, desiccating wildlife habitat in a land already parched. This is why so many water-dependent species have vanished, or are threatened or endangered. In Arizona, 20 of 35 surviving native fish species are endangered and one is already extinct. Mining presents yet another threat to the water supply, using up billions of gallons of groundwater over the course of years, and often contaminating it with pollutants.

Santa Rita Mts, © Larry Jones/USFS
The diversity of the “sacred” Santa Rita Mountains in the Coronado National Forest is threatened by mining interests.
The giant open-pit Rosemont Mine is planned for the Mountain Empire’s Santa Rita Mountains, where it would destroy habitat that is home to El Jefe and endangered ocelots. It would also decrease the water for the topminnow and other species in the Las Cienegas wetlands.
Two other mines are planned for the Patagonia Mountains in the center of the Mountain Empire. A Canadian company (ironically called Arizona Mining) is planning the Hermosa mine, which means beautiful in Spanish. There is nothing beautiful about this proposed silver mine: If done by the most economical open-pit method, it would gash a huge 4,000 foot wide hole in the mountains and dump the waste rock on the ground. A recent study by Earthworks and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance estimated that an open-pit mine here would take as much as 1.2 billion gallons of water per year from nearby streams and wells, harming wildlife as well as the local economy, which is based largely on ranching and tourism. Exploratory drilling (to prove the minerals are worth mining) is already taking place right next to Harshaw Creek, up against the protected activity center for a pair of threatened Mexican spotted owls and habitat for threatened yellow-billed cuckoos.
Thankfully, none of these projects are going unchallenged. Defenders and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance (PARA) are currently reviewing and preparing formal federal comments on a proposal by Arizona Mining to expand exploratory drilling onto Forest Service land. Last year, Defenders and PARA also joined in a lawsuit that overturned the Forest Service’s illegal approval of plans by another mining company, Regal Resources, to drill exploration cores along Harshaw Creek.
The Mountain Empire is an irreplaceable landscape in the Southwest. Defenders will keep working with local activists to monitor toxic spills and stop illegal mining that would harm the jaguars, ocelots, and other rare species that make it their home.
 Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office
Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office
As a jack-of-all trades in the Tucson Office, Rob collaborates with the Defenders Renewable Energy Group, helping evaluate and influence renewable energy policies and projects to ensure that renewable energy is developed wisely, with minimum harm to natural ecosystems. He also works on jaguar issues, helping plan for the eventual return of a viable population in the U.S., and he is the lead on Defenders efforts to safeguard Arizona’s Mountain Empire, a Defenders’ priority area surrounding the town of Patagonia. This area contains some of the last best native grasslands in the Southwest, along with important habitat for jaguar, Mexican spotted owl, and other endangered species.











