Oct 6, 2016 | Blog
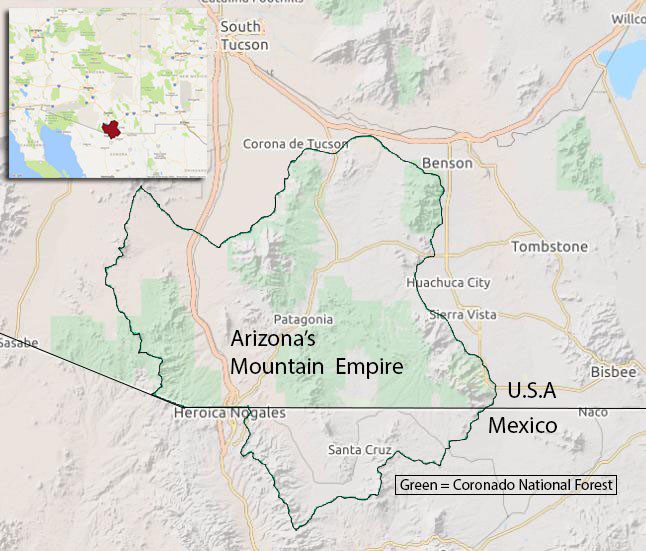
Imagine a little-known national treasure — a largely wild land home to ocelots, exotic and imperiled birds like elegant trogons and Mexican spotted owls, imperiled reptiles and amphibians like the threatened Chiricuahua leopard frog, and El Jefe, the only jaguar currently living in the United States. This is the Mountain Empire of southern Arizona, a place as special as Yosemite or Yellowstone, and worthy of international recognition. Extending across the border into northern Sonora, Mexico, this region is bounded by mountains that rise from the flat desert floor to touch the sky. With one of the richest concentrations of biodiversity in the U.S., the Mountain Empire is a sanctuary for imperiled species. But even a sanctuary can be threatened.

Mountain Empire, © Thunderforest
Refuges in the Sky
One reason the Mountain Empire has so many rare and unique species is the rugged sky island mountain ranges. Each range, like the iconic Santa Rita Mountains, south of Tucson, stands alone surrounded by desert flatlands like an island in the sea, with mountains so tall that they span climate zones from hot, dry desert to moist forests at higher altitudes. Together, these characteristics give the mountains their nicknames of “sky islands.” For many species, the sky islands are refuges where human impacts have been relatively small. Streams rise from the rocks, nurturing rare fish, frogs, snakes, and nesting habitat for birds like threatened yellow-billed cuckoos, southwestern willow fly catchers and hummingbirds.

Western yellow-billed cuckoo, © Creed Clayton/USFWS
There are so many hummingbird species in the Mountain Empire that the Tucson Audubon Society founded the Paton Hummingbird Center, dedicated to conserving hummingbirds and other local biodiversity.
Birders visit from countries around the world for the chance to see so many species in one place. One of Defenders’ board members, Dr. Ron Pulliam, works with the Mountain Empire group Borderlands Restoration to restore the plants that hummingbirds, bees, butterflies, and moths need along Harshaw and Sonoita Creeks in the Patagonia Mountains. The globally imperiled Patagonia eyed silk moth, once widespread in native grasslands, is now making its last U.S. stand in the Patagonia Mountains. The threatened southwestern willow flycatcher, once common near Tucson in now-vanished gallery forest along the Santa Cruz River, is today found higher up in riparian vegetation along still-flowing mountain streams.
One of the gems of the Mountain Empire is the Las Cienegas National Conservation Area: 45,000 acres of rolling grasslands, oak-studded hills, along with the Cienegas Creek wetlands. This is home to the world’s largest population of endangered Gila topminnow and other federally threatened and endangered fish, frogs and snakes. Las Cienegas provides a vital corridor of protected lands that connects the Santa Rita and Whetstone sky islands.
The most revered animal in the Mountain Empire is El Jefe, a powerful male jaguar. Video of him prowling along a stream in the Santa Rita Mountains recently went viral, with at least 20 million viewers. He and other jaguars and ocelots most likely came north to the U.S. from Sonora, Mexico in the past decade, travelling along sky island mountain corridors with little human activity.

Jaguar, © Barry Draper
Threats to the Empire
Sadly, as much healthy habitat as there is in this region, there’s also a problem: Industrial mining. The Mountain Empire is riddled with old abandoned mines and grandiose plans for new ones. As you can imagine, mining has a massive impact on an ecosystem, from the land itself, to the noise that can scare wildlife away, to the traffic that would come in and out of the mining project. And perhaps most importantly, there’s the water.
Throughout the Southwest, so much groundwater has been pumped for agriculture, industry, and towns and cities that water tables have dropped and streams and ponds have dried up, desiccating wildlife habitat in a land already parched. This is why so many water-dependent species have vanished, or are threatened or endangered. In Arizona, 20 of 35 surviving native fish species are endangered and one is already extinct. Mining presents yet another threat to the water supply, using up billions of gallons of groundwater over the course of years, and often contaminating it with pollutants.

Santa Rita Mts, © Larry Jones/USFS
The diversity of the “sacred” Santa Rita Mountains in the Coronado National Forest is threatened by mining interests.
The giant open-pit Rosemont Mine is planned for the Mountain Empire’s Santa Rita Mountains, where it would destroy habitat that is home to El Jefe and endangered ocelots. It would also decrease the water for the topminnow and other species in the Las Cienegas wetlands.
Two other mines are planned for the Patagonia Mountains in the center of the Mountain Empire. A Canadian company (ironically called Arizona Mining) is planning the Hermosa mine, which means beautiful in Spanish. There is nothing beautiful about this proposed silver mine: If done by the most economical open-pit method, it would gash a huge 4,000 foot wide hole in the mountains and dump the waste rock on the ground. A recent study by Earthworks and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance estimated that an open-pit mine here would take as much as 1.2 billion gallons of water per year from nearby streams and wells, harming wildlife as well as the local economy, which is based largely on ranching and tourism. Exploratory drilling (to prove the minerals are worth mining) is already taking place right next to Harshaw Creek, up against the protected activity center for a pair of threatened Mexican spotted owls and habitat for threatened yellow-billed cuckoos.
Thankfully, none of these projects are going unchallenged. Defenders and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance (PARA) are currently reviewing and preparing formal federal comments on a proposal by Arizona Mining to expand exploratory drilling onto Forest Service land. Last year, Defenders and PARA also joined in a lawsuit that overturned the Forest Service’s illegal approval of plans by another mining company, Regal Resources, to drill exploration cores along Harshaw Creek.
The Mountain Empire is an irreplaceable landscape in the Southwest. Defenders will keep working with local activists to monitor toxic spills and stop illegal mining that would harm the jaguars, ocelots, and other rare species that make it their home.
 Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office
Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office
As a jack-of-all trades in the Tucson Office, Rob collaborates with the Defenders Renewable Energy Group, helping evaluate and influence renewable energy policies and projects to ensure that renewable energy is developed wisely, with minimum harm to natural ecosystems. He also works on jaguar issues, helping plan for the eventual return of a viable population in the U.S., and he is the lead on Defenders efforts to safeguard Arizona’s Mountain Empire, a Defenders’ priority area surrounding the town of Patagonia. This area contains some of the last best native grasslands in the Southwest, along with important habitat for jaguar, Mexican spotted owl, and other endangered species.

Aug 15, 2016 | Blog
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
AUGUST 15, 2016

Ocelot, photo US FWS
TUCSON, Ariz. – The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service released a recovery plan that will guide restoration and protection of the ocelot populations in Arizona and Texas and in bordering Mexican states of Sonora and Tamaulipas. The ultimate goal of the plan is to increase the number of ocelots in both nations, protect their habitat and create connecting habitat corridors between Arizona and Sonora and between Texas and Tamaulipas. This unique endangered cat ranges as far south as Argentina, but in the U.S. is found only in two small areas of Arizona and Texas.
Statement by Rob Peters, senior Southwest representative for Defenders of Wildlife
“It is encouraging to see a plan that sets quantitative targets for ocelot recovery – 1,200 animals in the Texas-Tamaulipas area and 1,000 in the Arizona-Sonora. To reach these targets, wildlife agencies must decrease deaths and increase important thorn scrub habitat, goals that will require funding and binational cooperation. A serious question is whether there is the political will to provide the necessary resources and limit development.
“Big threats to ocelot recovery in the U.S. include giant open-pit mines like the Rosemont and Hermosa proposed in ocelot habitat in Arizona. In south Texas, three huge liquefied natural gas export terminals are planned right next to the Atascosa National Wildlife Refuge. One terminal would sit on – and possibly sever – an ocelot travel corridor identified by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as vital to the recovery of the ocelot population in Texas. This recovery plan is a starting point, but it will only succeed if harmful developments are stopped and sufficient resources are provided for key conservation actions. Defenders will vigilantly monitor proposed development activities that threaten the future of the ocelot in the United States.”
Background:
U.S. ocelot populations, once extending into Arkansas and Louisiana, have shrunk to a small patch of southern Texas, with perhaps 50 animals, and southern Arizona, where only five animals have been detected since 2009. Ocelots, found in every country south of the United States except Chile, are endangered throughout their range. Some 95 percent of the cats’ native habitat in the U.S. has become urbanized or has been converted to agriculture.
Listed under the Endangered Species Act in 1982 as endangered, the species was initially pushed to the brink of extinction due to habitat loss and overhunting. Now, collisions with vehicles and insufficient habitat are keeping ocelot population numbers in the U.S. low. Mines and liquefied natural gas plants are important new threats.

Sep 9, 2015 | Blog
 The Patagonia Area Resource Alliance and Defenders of Wildlife were in federal court in Tucson last Thursday to present oral arguments against the Forest Service’s unlawful approval of a mining exploration project in the Patagonia Mountains on the Coronado National Forest.
The Patagonia Area Resource Alliance and Defenders of Wildlife were in federal court in Tucson last Thursday to present oral arguments against the Forest Service’s unlawful approval of a mining exploration project in the Patagonia Mountains on the Coronado National Forest.
Over 20 people attended the court hearing in support of PARA, Defenders of Wildlife and the Patagonia Mountains.
Canadian mining company Regal Resources’ Sunnyside Project involves drilling six exploratory holes for copper deposits up to 6,500 feet deep roughly five miles from the Town of Patagonia.
The Forest Service issued a “categorical exclusion” decision which essentially fast-tracked the mineral drilling exploration and approved the project without doing any environmental assessments. The decision authorized Regal Resources to run drilling for one year, with a seven month stoppage during the breeding seasons of the Mexican spotted owl and Yellow-billed cuckoo.
Defenders of Wildlife Lawyer Jay Tutchton argued that the Forest Service’s approval of the Sunnyside project violates environmental laws and poses a potential threat to local, endangered species. The extensive mineral drilling and construction would run 24 hours a day, seven days a week with total project operations and reclamation lasting up to 3 years.

Mexican Spotted Owl ©Gooch Goodwin
The Patagonia Mountains support some of the world’s most threatened and endangered wildlife, including the jaguar, ocelot, lesser long-nosed bat, Mexican spotted owl, and yellow-billed cuckoo. Of particular concern is the Mexican spotted owl “Protected Activity Center” (PAC), prime habitat which is supposed to have the greatest protection by law and is occupied by the owls year-round. One of the project’s proposed drilling sites is less than 200 yards from a “nesting core area” of the PAC. The noise caused by the drills would be louder than a chainsaw and would disrupt about one-third of the Mexican spotted owls’ PAC, as well as the migratory corridors of jaguars and ocelots, Tutchton argued.
The Forest Service asked the court to dismiss the complaint. Forest Service lawyer Julia Thrower claimed the decision to grant a categorical exclusion complied with the National Environmental Protection Act and was not arbitrary or capricious.
“We’re optimistic that the judge will agree that the Forest Service’s attempt to avoid extra paperwork by skipping environmental assessments violates the law and places local, imperiled wildlife in even more jeopardy,” said Wendy Russell of the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance.
U.S. District Court Judge Rosemary Marquez said that she would take the matter under advisement and would issue her ruling before the proposed October 1 start date.

Jan 13, 2015 | Blog
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Plug Pulled on Proposed “Sunnyside” project in Arizona’s Coronado National Forest
Tucson, Ariz. — Today the U.S. Forest Service temporarily put the brakes on an environmentally hazardous mining project in southern Arizona’s Coronado National Forest that it previously approved in August. The Forest Service’s decision follows a similar move by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, which had originally given the project the green light in August and then withdrew its approval in December. The agency decisions to withdraw their approvals of the Canadian mining company Regal Resources’ “Sunnyside Project” are based on the project’s potential violation of multiple environmental laws.

photo by Nathan Rupert
“The agencies knew from the beginning that this project could have a devastating impact on the local wildlife and habitat in this unique corner of the country,” said Rob Peters of Defenders of Wildlife. “The Coronado is home to an incredible diversity of imperiled species like the jaguar, ocelot and yellow-billed cuckoo, all which are already at risk from multiple projects in the region.”
“No one understood why they approved this project to begin with, but for the sake of Patagonia’s residents and wildlife, we are glad to see that they’ve reconsidered,” added Peters.
In October conservation groups Defenders of Wildlife and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance filed a lawsuit claiming the federal agencies’ approvals the Sunnyside project violated environmental laws and posed a threat to endangered species and the safety of drinking water for local residents.
“Sunnyside could have been a disaster not only for our region’s unique wildlife, but also for the residents living directly downstream and the municipal watershed of the town of Patagonia,” said Wendy Russell of the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance. “Projects like Sunnyside use and abuse a tremendous amount of the local water supply and create long-term destruction of wildlife habitat. The people and wildlife of our national forests deserve more, and the agencies know that.”
Click to hear from environmental attorneys on why they sue.
###
Contact: Courtney Sexton, csexton@defenders.org, 202-772-0253
Wendy Russell, wendy@patagoniaalliance.org, 520-477-2308
Defenders of Wildlife is dedicated to the protection of all native animals and plants in their natural communities. With more than 1.1 million members and activists, Defenders of Wildlife is a leading advocate for innovative solutions to safeguard our wildlife heritage for generations to come. For more information, visit www.defenders.org and follow us on Twitter @DefendersNews.
The Patagonia Area Resource Alliance is a citizen watchdog organization that monitors the activities of mining companies, as well as ensures government agencies’ due diligence, to make sure their actions have long-term, sustainable benefits to our public lands, our water, and the town of Patagonia. For more information visit www.patagoniaalliance.org and follow us on Twitter @PARAalliance.

Oct 29, 2014 | Blog
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
October 29, 2014
Contact: Courtney Sexton, csexton@defenders.org, 202-772-0253
Wendy Russell, wendy@patagoniaalliance.org, 520-477-2308
Groups file complaint against Forest Service and Fish and Wildlife Service for approval of mineral drilling project in Arizona’s Coronado National Forest
TUCSON, ARIZ. – Defenders of Wildlife and the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance today asked a federal court to hold the United States Forest Service and United States Fish and Wildlife Service accountable for their unlawful approval of the “Sunnyside” mineral exploration drilling project in southern Arizona’s Coronado National Forest, in the Alum Gulch area of the Patagonia Mountains. The groups say the approval of the Canadian mining company Regal Resources’ Sunnyside Project violates environmental laws and poses a potential threat to endangered species and the safety of drinking water for local residents. The Sunnyside Project involves drilling multiple exploratory holes up to 6,500 feet deep in one of the most biologically diverse mountain ranges in Arizona. The extensive drilling and construction would run 24/7 for months on end, and the total project operations could last up to 3 years.

Mexican spotted owl, ©Gooch Goodwin
The Coronado National Forest, the Patagonia Mountains and the watersheds in this region support some of the world’s most imperiled wildlife, including the jaguar, ocelot, lesser long-nosed bat, Mexican spotted owl, and yellow-billed cuckoo. Of particular concern is the Mexican spotted owl “Protected Activity Center” (PAC) in the Alum Gulch area, a site which is supposed to have the greatest protection of the law. One of the project’s proposed drilling sites is only one-tenth of a mile from the “nesting core area” of this PAC.
“The potential damage from the Sunnyside Project, especially coupled with other damaging mining projects in the region, could have devastating impacts on this imperiled wildlife and the habitat they depend on, as well as the water supply for local residents,” said Rob Peters of Defenders of Wildlife. “This is a national forest and imperiled wildlife and their habitats on the forest should be protected— not polluted by expanded drilling operations.”

Ocelot, Leopardus pardalis. photo US FWS
Patagonia area residents are dependent on water originating from Alum Gulch, an area which is also designated as critical habitat for the jaguar and Mexican spotted owl. The imperiled ocelot, lesser long-nosed bat, and yellow-billed cuckoo have also been observed near the project area.
“The Sunnyside Project could have tremendous adverse impacts on local wildlife and local residents, affecting the floodplains and the municipal watershed of the town of Patagonia,” said Wendy Russell of the Patagonia Area Resource Alliance. “The drilling will require 12,500 gallons of water per day, an amount approximately equal to ten percent of the daily water usage of the Town of Patagonia. This project threatens not only endangered wildlife, but our community’s water, health and safety.”
Click to hear from environmental attorneys on why they sue.
###
Defenders of Wildlife is dedicated to the protection of all native animals and plants in their natural communities. With more than 1.1 million members and activists, Defenders of Wildlife is a leading advocate for innovative solutions to safeguard our wildlife heritage for generations to come. For more information, visit www.defenders.org and follow us on Twitter @DefendersNews.
The Patagonia Area Resource Alliance is a citizen watchdog organization that monitors the activities of mining companies, as well as ensures government agencies’ due diligence, to make sure their actions have long-term, sustainable benefits to our public lands, our water, and the town of Patagonia. For more information visit www.patagoniaalliance.org and follow us on Twitter @PARAalliance.





 Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office
Rob Peters, Senior Representative, Southwest Office















